Managed Language - 자바, C#, python
Unmanaged Language - C, C++, asm
managed의 뜻은 메모리 관리를 자동으로 하냐 직접 해주냐임
두 영역별 언어 1개씩은 할 줄 아는게 중요
JDBC
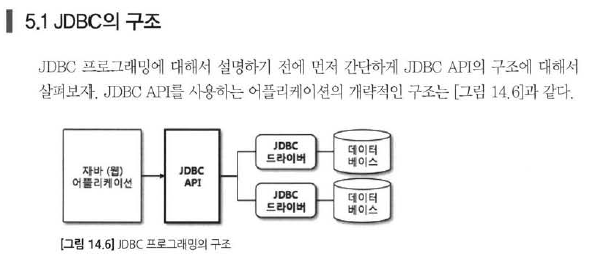
JDBC 드라이버 가져오는 법


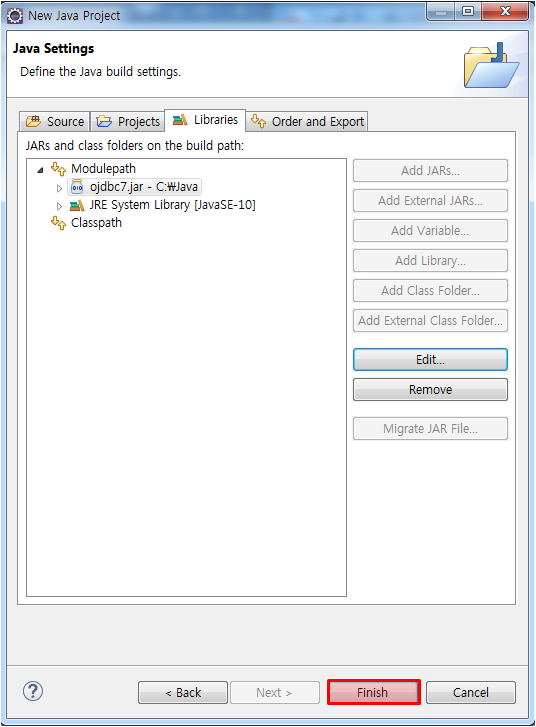


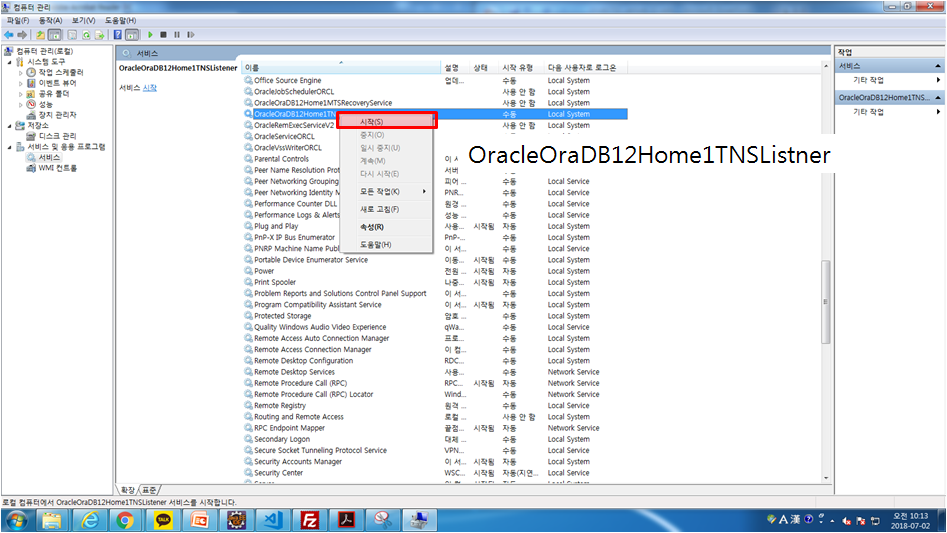
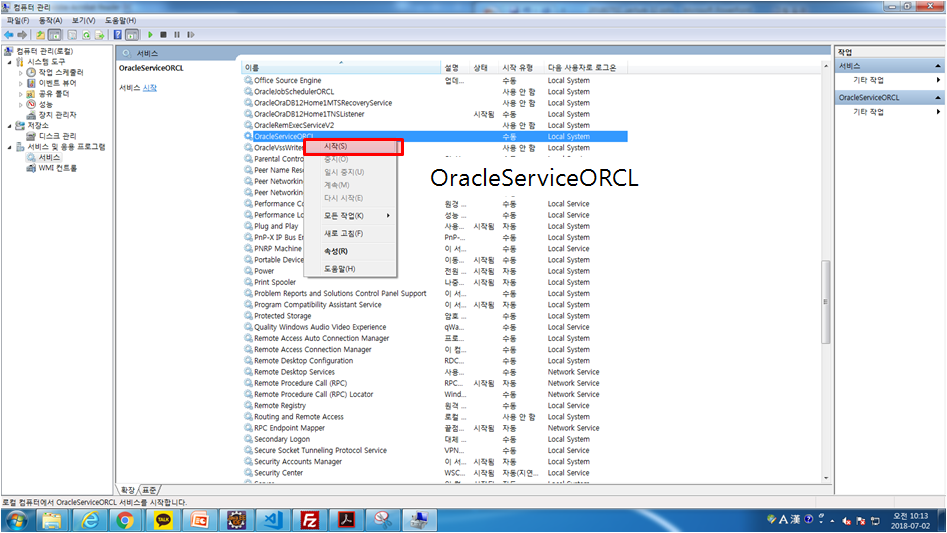


JDBC URL, 드라이브로딩, 커넥션

DML 처리
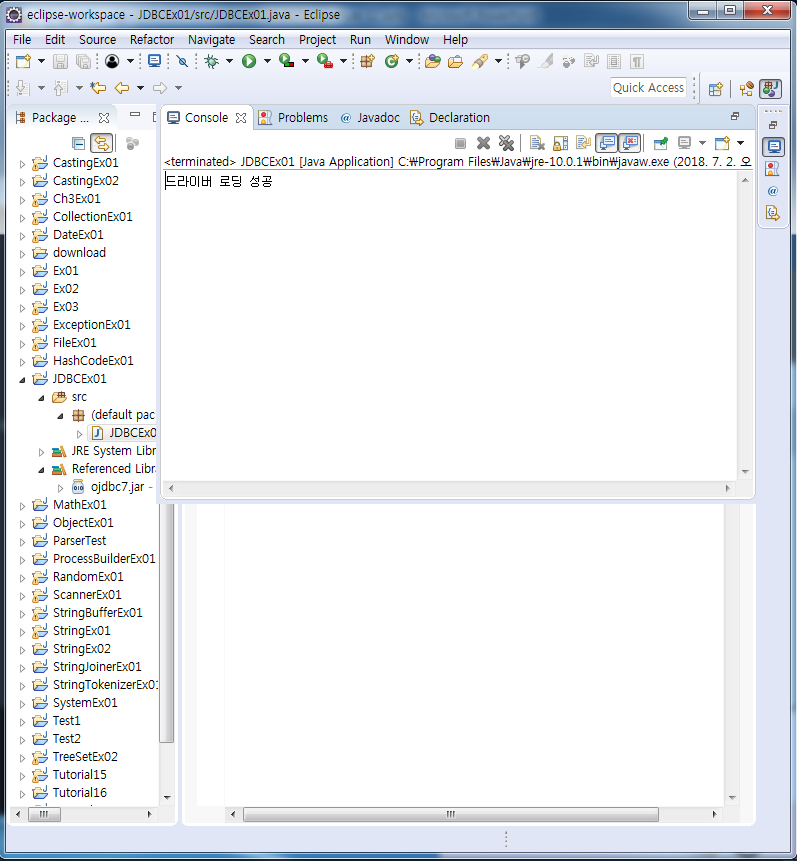
JDBCEx01 - 드라이버 로딩 법
public class JDBCEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 드라이버 - 라이브러리 내의 클래스
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
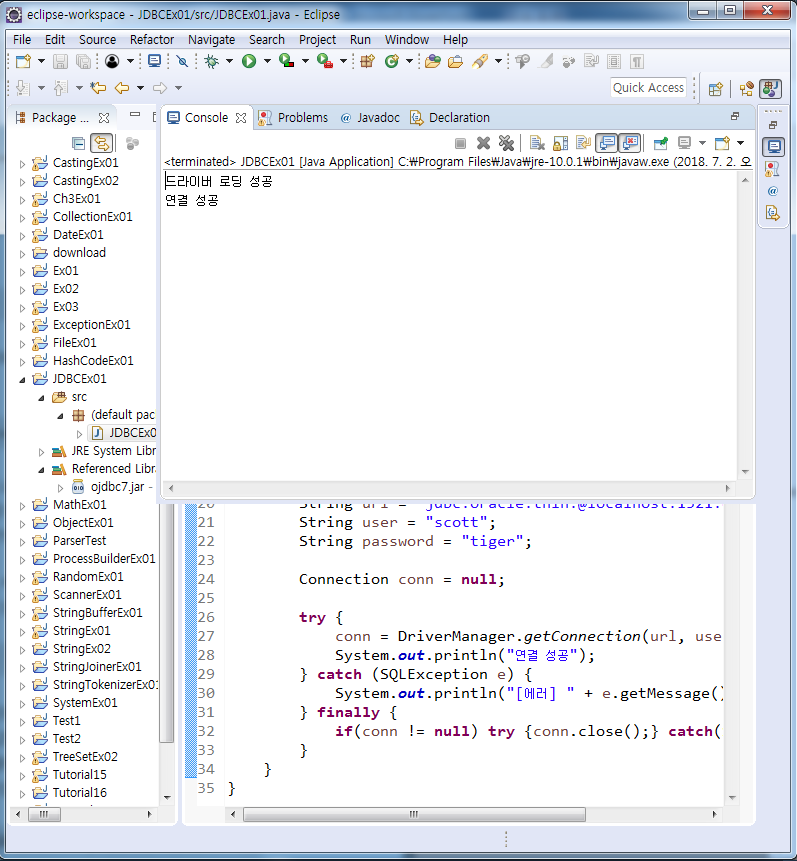
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
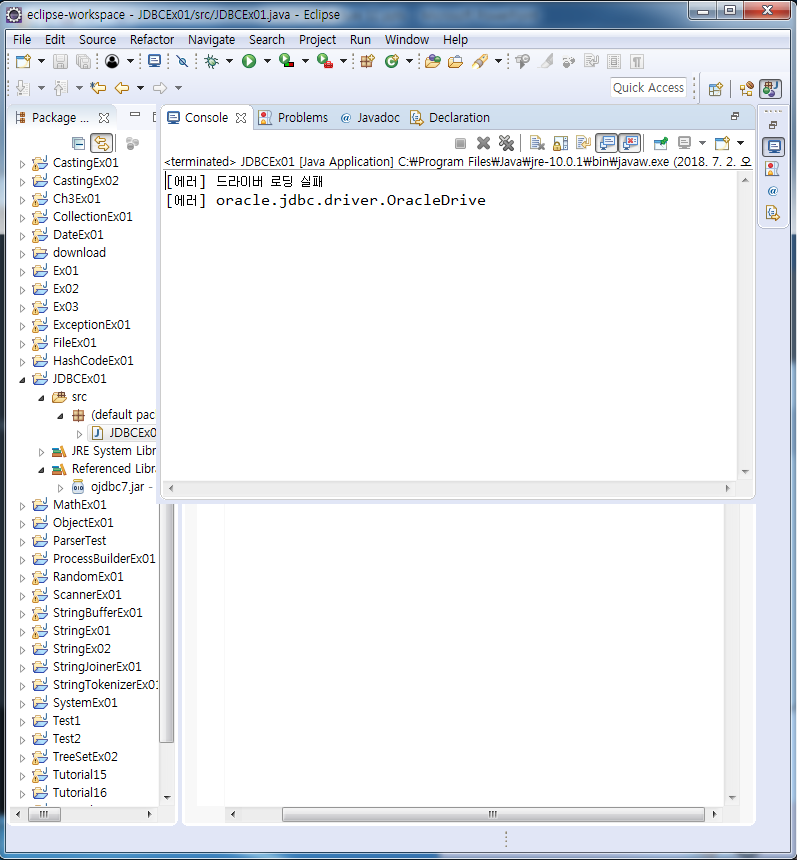
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
public class JDBCEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 드라이버 - 라이브러리 내의 클래스
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDrive");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
}
}
}
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JDBCEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 드라이버 - 라이브러리 내의 클래스
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
}
// localhost : 127.0.0.1
// 각자의 아이피 : 192.168.xxx.xxx
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
드라이버로딩, 컨넥션
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JDBCEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 드라이버 - 라이브러리 내의 클래스
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
}
// localhost : 127.0.0.1
// 각자의 아이피 : 192.168.xxx.xxx
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orc";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}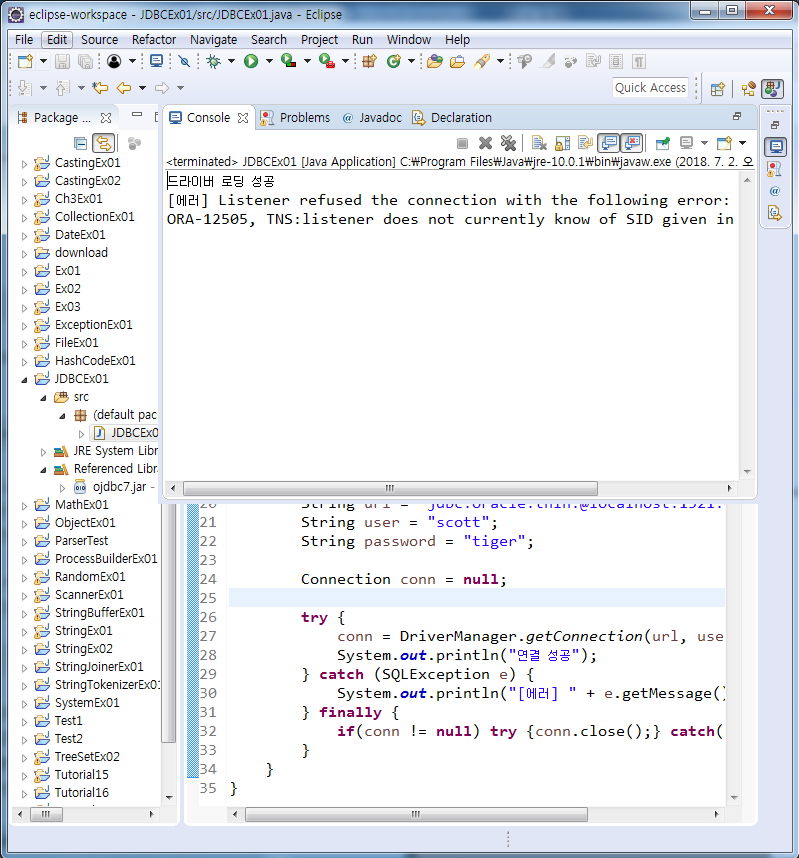
로딩 성공, 커넥션 실패
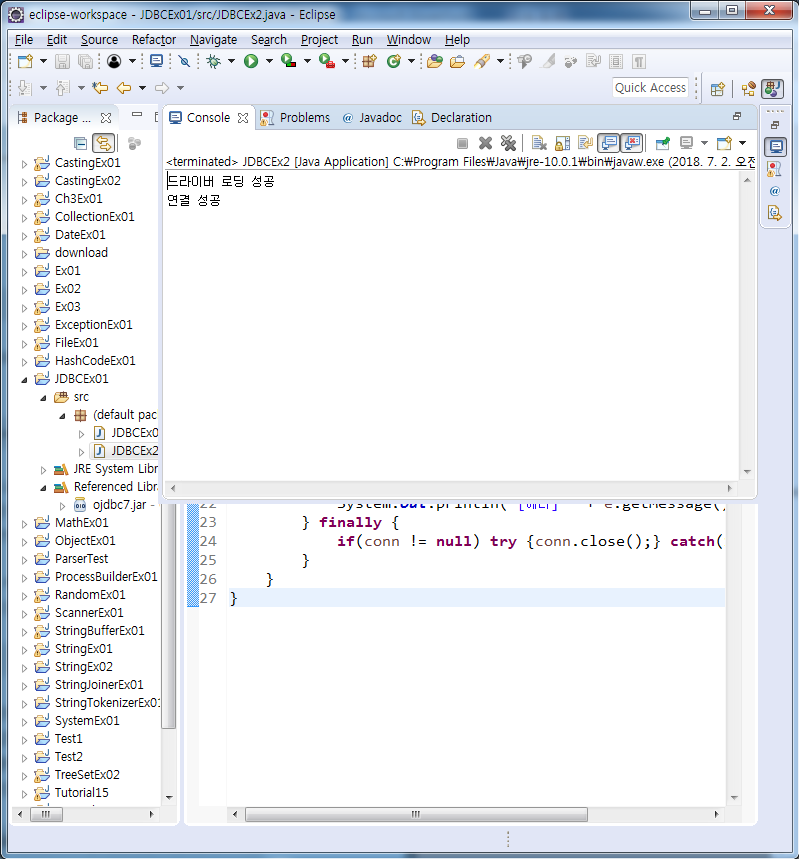
JDBCEx2 - 드라이버 로딩 후 커넥션 하는 법
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class JDBCEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
JDBCEx01을 깔끔하게 줄임
Statement를 사용한 쿼리 실행
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
// sql 저장 실행 공간
stmt = conn.createStatement();
stmt.executeUpdate("insert into dept2 values (90, '개발', '서울')");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}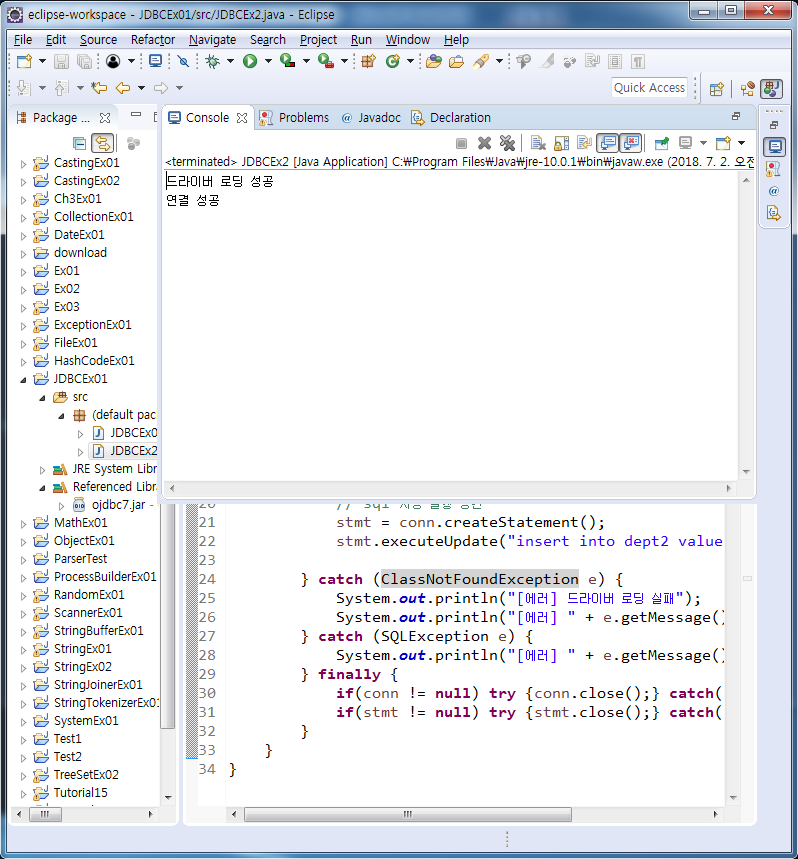

import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
// sql 저장 실행 공간
stmt = conn.createStatement();
stmt.executeUpdate("insert into dept3 values (90, '개발', '서울')");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}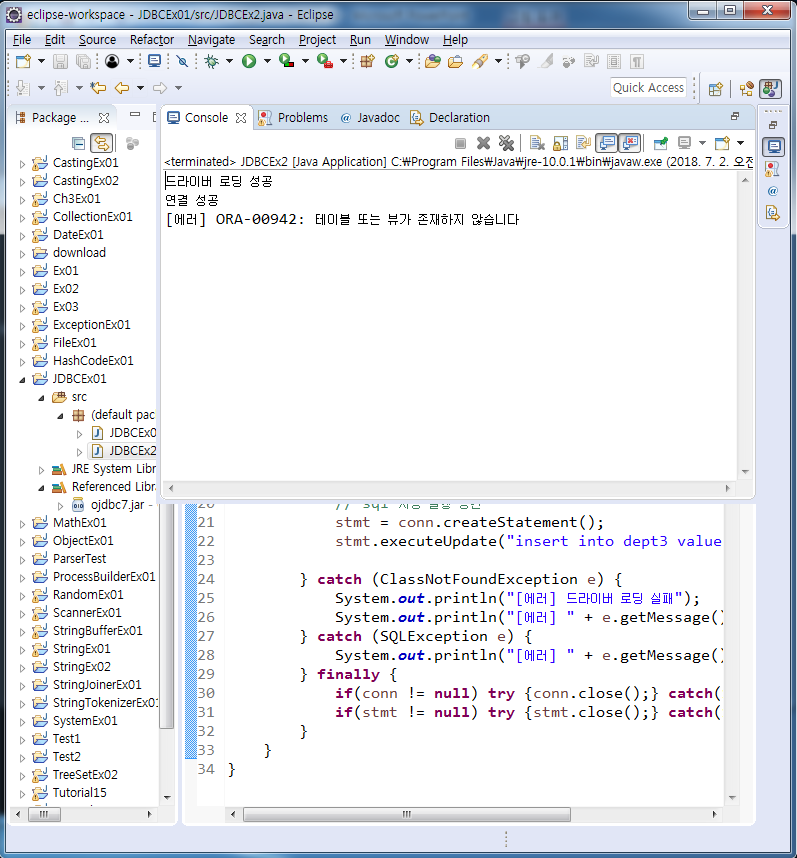
dept3에 데이터를 추가하라고 명령 후 발생한 에러. SQL에서 발생한 에러 메세지를 getMessage()를 통해서 잡아와서 출력해준다
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
// sql 저장 실행 공간
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// autocommit(); - 트랜잭션 관계임을 기억할 것
String sql = "insert into dept2 values (90, '개발', '서울')";
int result = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("입력 데이터 갯수 : " + result);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}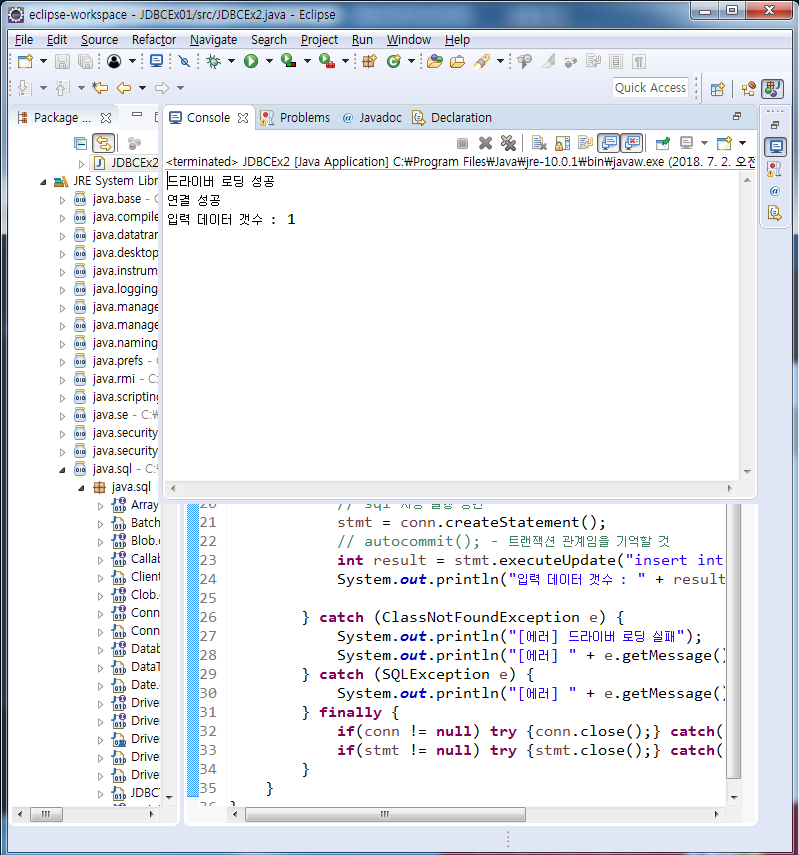
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
// sql 저장 실행 공간
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// autocommit(); - 트랜잭션 관계임을 기억할 것
String deptno = "60";
String dname = "연구";
String loc = "대전";
String sql = "insert into dept2 values (" + deptno + ", '" + dname + "', '" + loc + "')";
System.out.println(sql);
//int result = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
//System.out.println("입력 데이터 갯수 : " + result);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
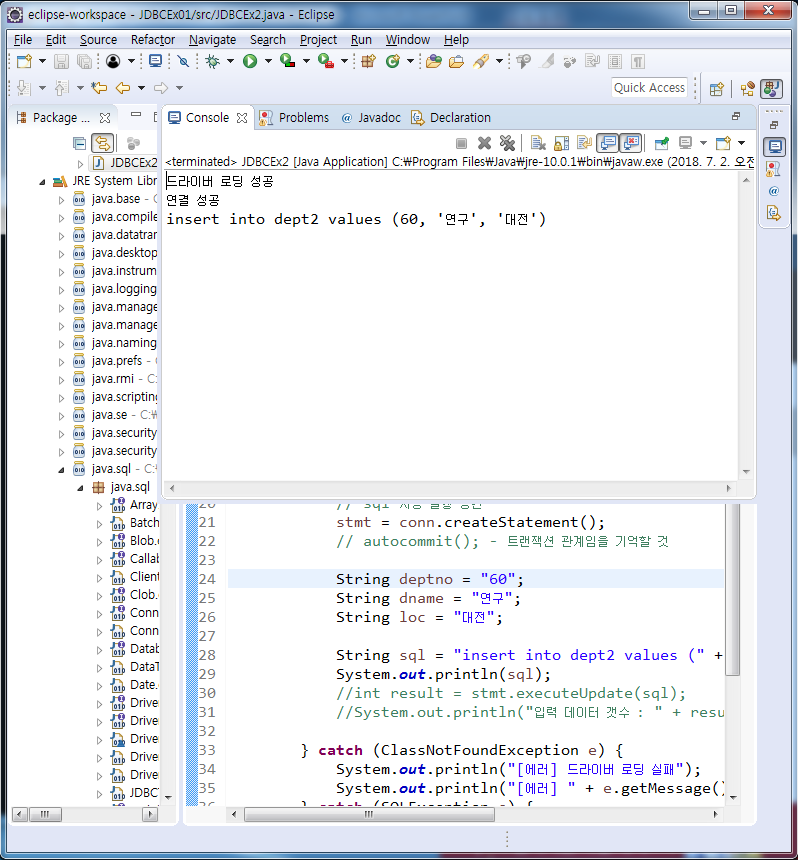
sql 구문이 잘 입력되었음을 출력하여 확인하고 문제 없으면 비로서 데이터를 입력시키는 구문을 실행시킨다
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
// sql 저장 실행 공간
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// autocommit(); - 트랜잭션 관계임을 기억할 것
String deptno = "60";
String dname = "연구";
String loc = "대전";
String sql = "insert into dept2 values (" + deptno + ", '" + dname + "', '" + loc + "')";
System.out.println(sql);
int result = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("입력 데이터 갯수 : " + result);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}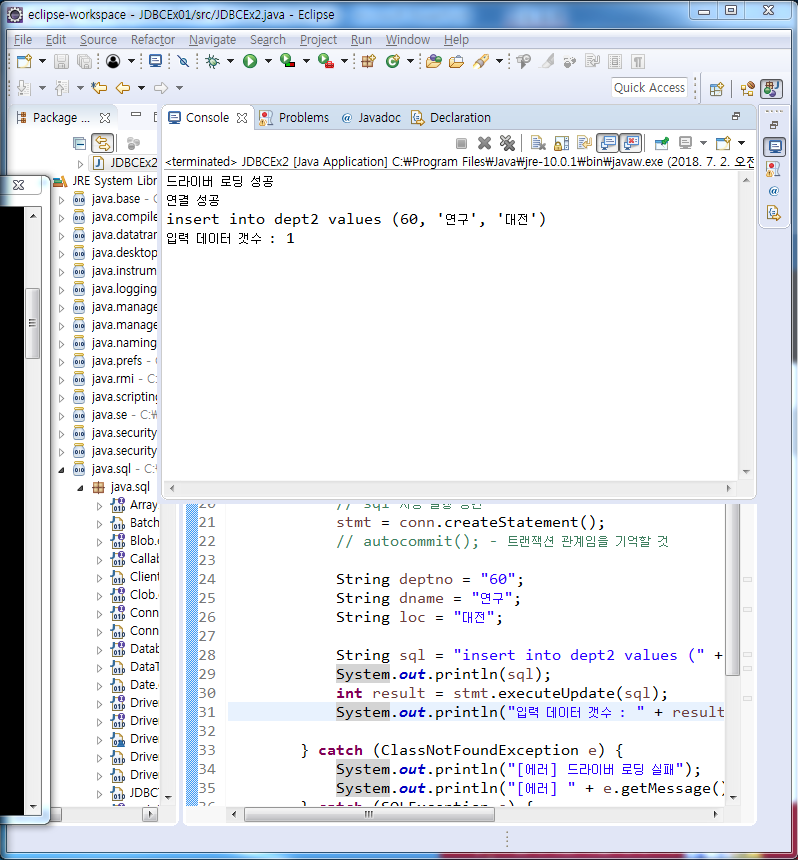

import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
// sql 저장 실행 공간
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// autocommit(); - 트랜잭션 관계임을 기억할 것
String deptno = "60";
String dname = "연구";
String loc = "대전";
//String sql = "insert into dept2 values (" + deptno + ", '" + dname + "', '" + loc + "')";
String sql = String.format("insert into dept2 values (%s, '%s', '%s')", deptno, dname, loc);
System.out.println(sql);
int result = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("입력 데이터 갯수 : " + result);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
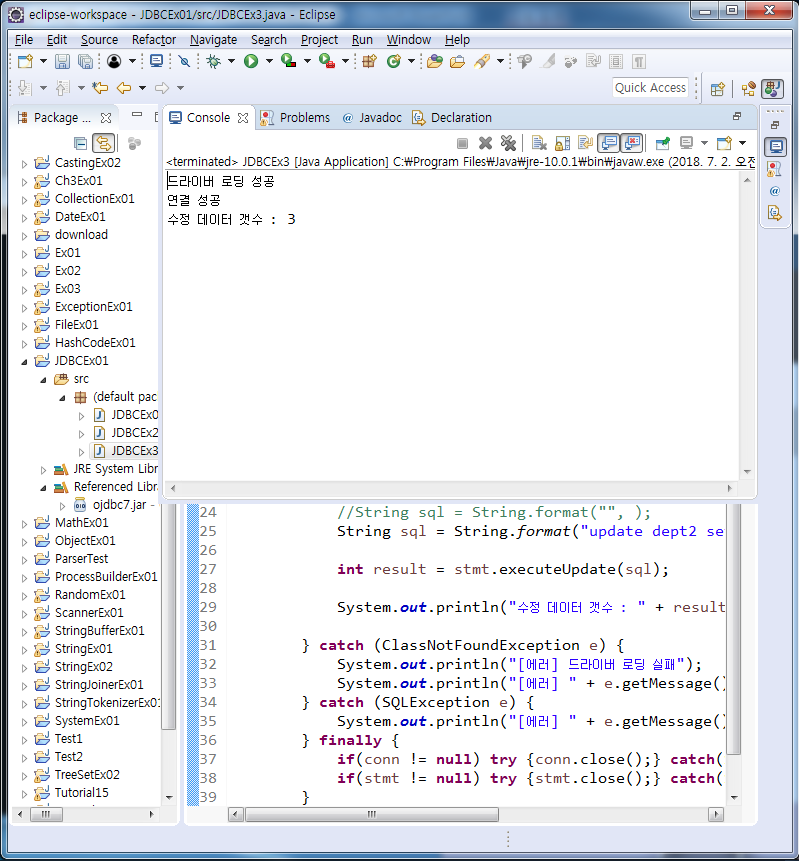
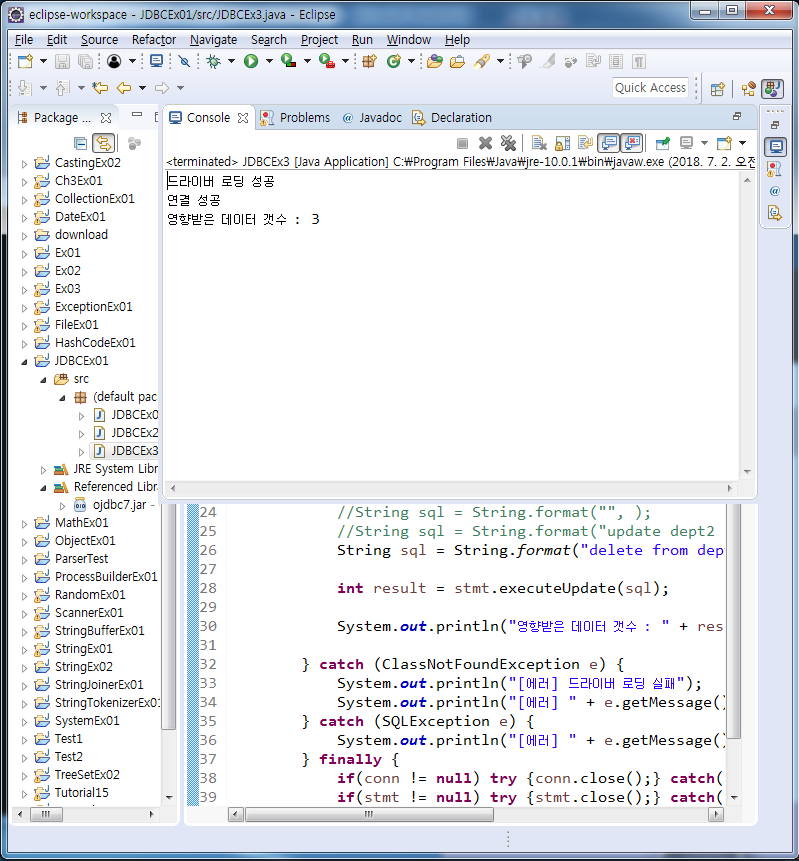
JDBCEx3 - sql update구문 명령 법
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// update ..
//String sql = String.format("", );
String sql = String.format("update dept2 set dname='%s' where deptno=%s ", "총무", "60");
int result = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("수정 데이터 갯수 : " + result);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
// update ..
//String sql = String.format("", );
//String sql = String.format("update dept2 set dname='%s' where deptno=%s ", "총무", "60");
String sql = String.format("delete from dept2 where deptno=%s ", "60");
int result = stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("영향받은 데이터 갯수 : " + result);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
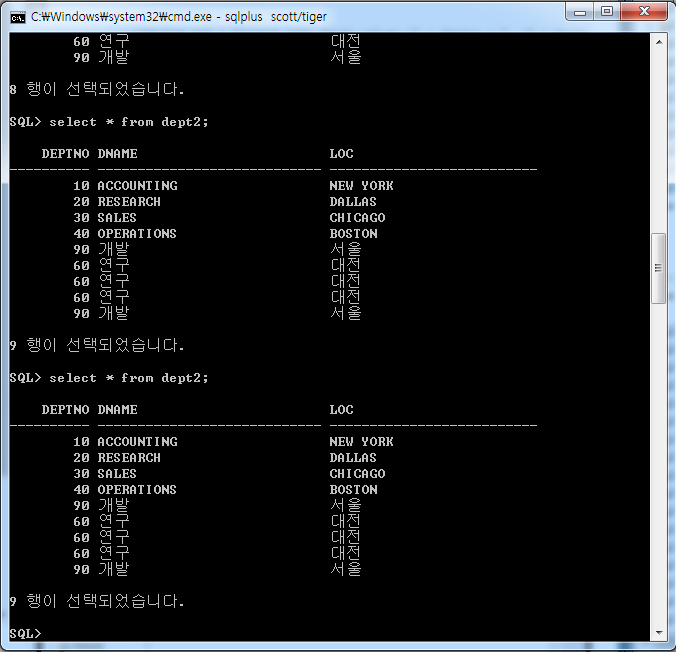
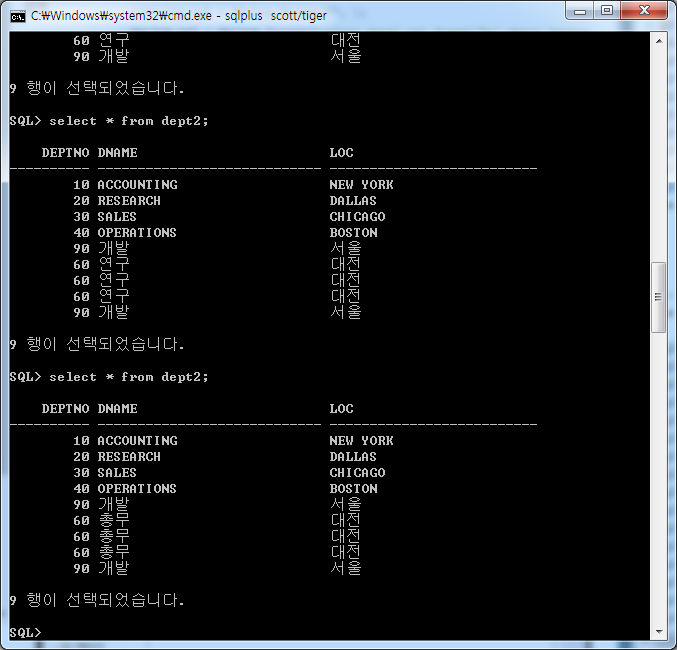
60번 부서를 지운다

60번 부서 지워졌다
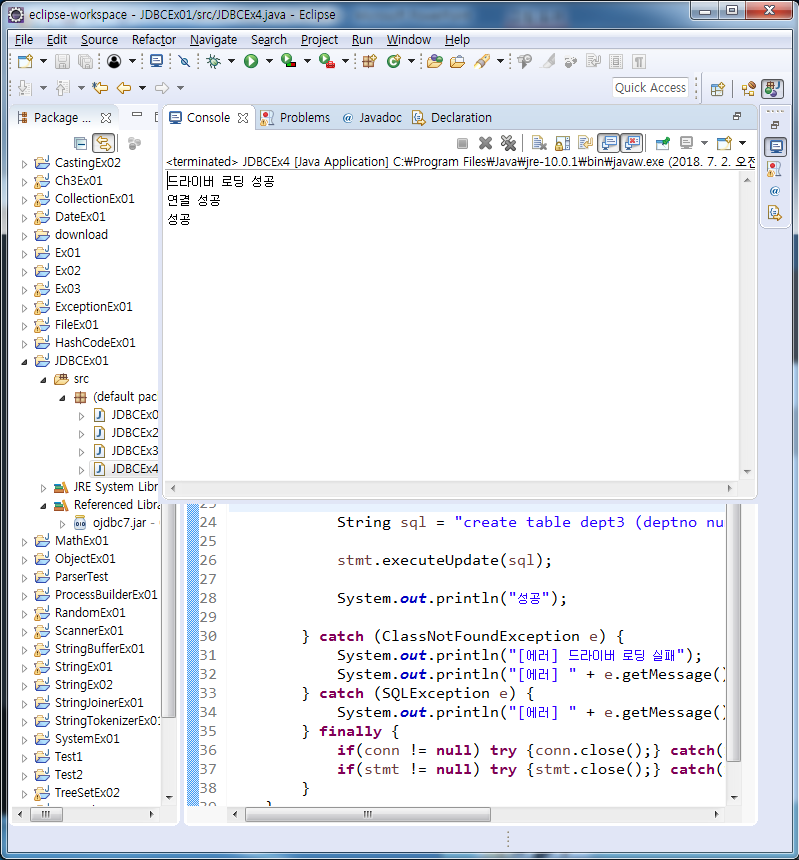
JDBCEx4 - DDL 처리, sql create 구문 명령 법
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "create table dept3 (deptno number(2), dname varchar2(14), loc varchar2(13))";
stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("성공");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}

import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//String sql = "create table dept3 (deptno number(2), dname varchar2(14), loc varchar2(13))";
StringBuffer sql = new StringBuffer("create table dept4 (");
sql.append(" deptno number(2), ");
sql.append(" dname varchar2(14), ");
sql.append(" loc varchar2(13)");
sql.append(" )");
stmt.executeUpdate(sql.toString());
System.out.println("성공");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}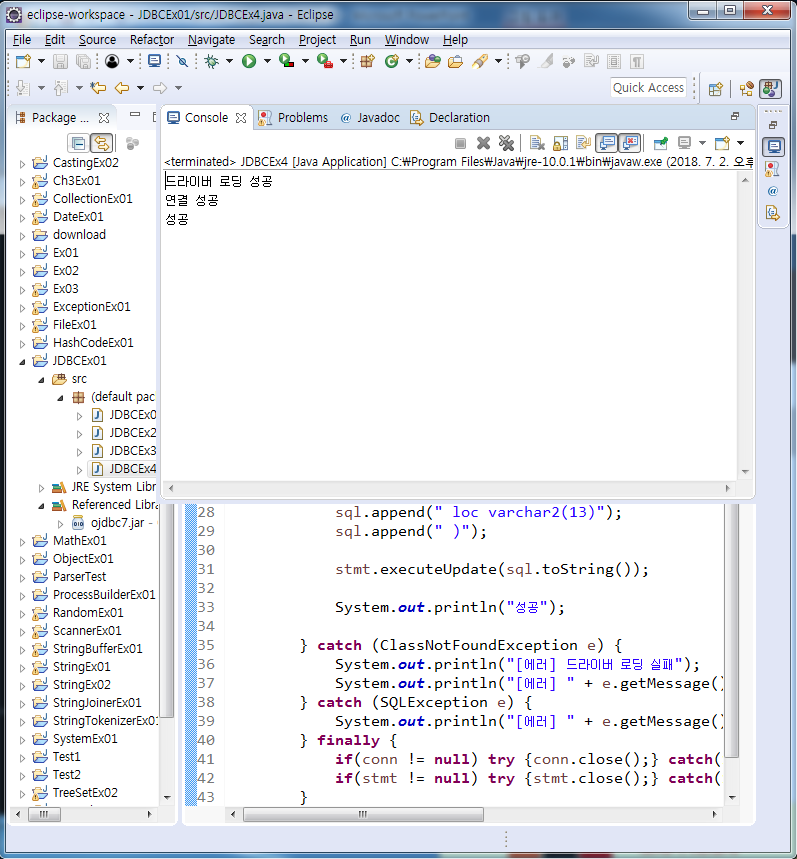
간결하게 만듬

executeUpdate는 insert, update, delete, create가 되는데 select만 안된다.
ResultSet에서 값 읽어오기
select는 ResultSet executeQuery(Stirng query)를 사용해야 한다.
Statement의 executeQuery() 메서드는 SELECT 쿼리를 실행할 때 사용되며, SELECT 쿼리의 실행 결과를 java.sql.ResultSet 객체에 담아서 리턴한다. 따라서, ResultSet이 제공하느 ㄴ메서드를 사용해서 결과값을 읽어 올 수 있다.
ResultSet 클래스는 next() 메서드를 제공하는데, next() 메서드를 사용해서 SELECT 결과의 존재 여부를 확인할 수 있다.
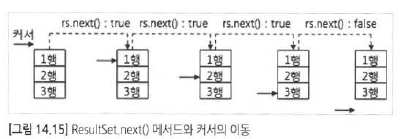
int나 float, double등은 형변환 시켜서 값 불러오면 된다 getString만 외우자


JDBCEx5 - sql Select 명령 법
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
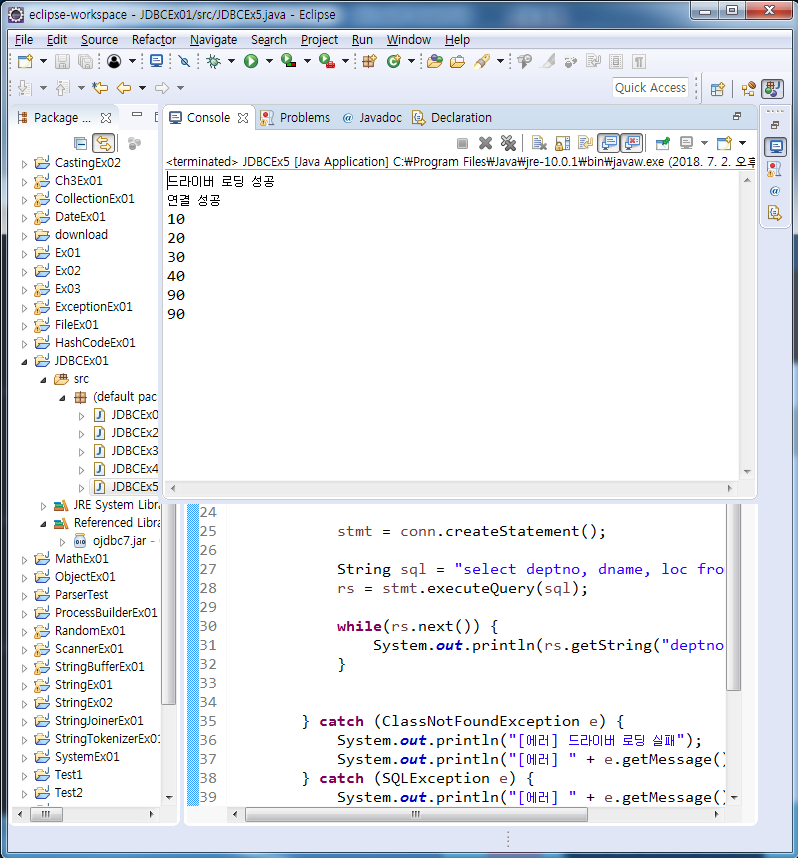
String sql = "select deptno, dname, loc from dept2";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()) { //행
System.out.println(rs.getString("deptno")); //컬럼
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(rs != null) try {rs.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
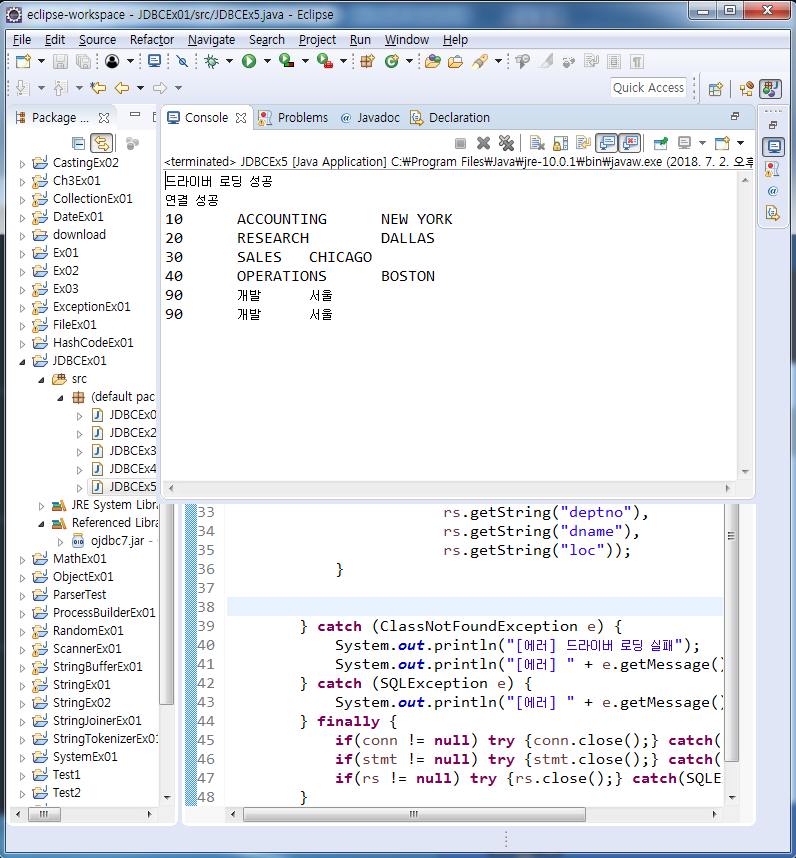
String sql = "select deptno, dname, loc from dept2";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()) { //행
//System.out.println(rs.getString("deptno")); //컬럼
System.out.printf("%s\t%s\t%s\n",
rs.getString("deptno"),
rs.getString("dname"),
rs.getString("loc"));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(rs != null) try {rs.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "select deptno, dname, loc from dept2";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
while(rs.next()) { //행
//System.out.println(rs.getString("deptno")); //컬럼
//System.out.printf("%s\t%s\t%s\n",
// rs.getString("deptno"),
// rs.getString("dname"),
// rs.getString("loc"));
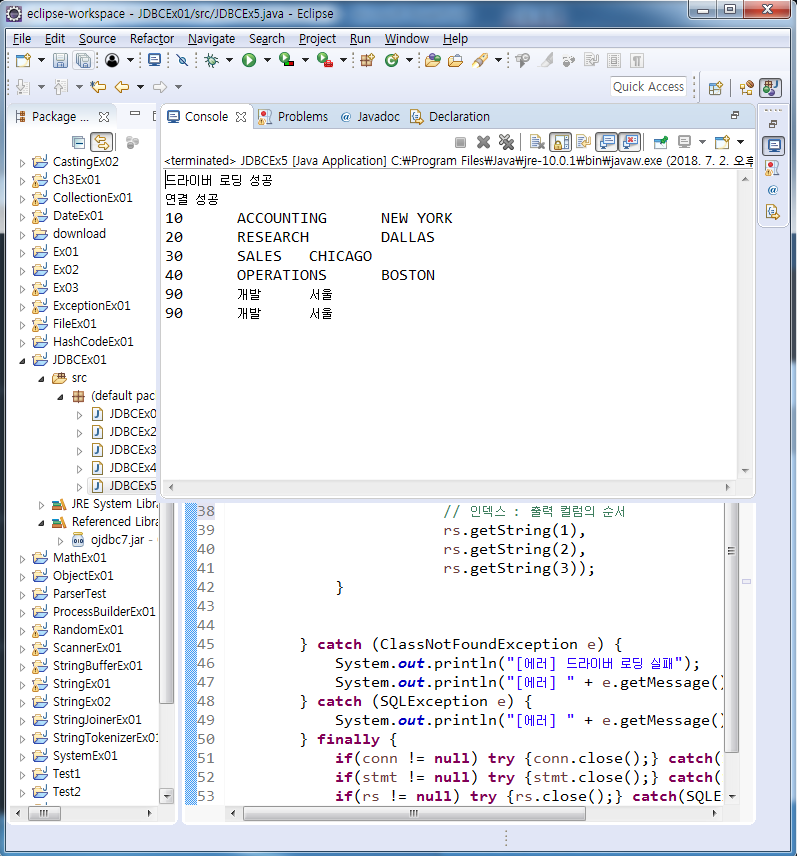
System.out.printf("%s\t%s\t%s\n",
// 인덱스 : 출력 컬럼의 순서
rs.getString(1),
rs.getString(2),
rs.getString(3));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(rs != null) try {rs.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
JDBCEx6
10번 부서의 사원번호, 사원명, 부서번호, 연봉을 출력하는 구문을 생성하시오
연봉 = sal*12 + comm(null조심)
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
String sql = "select empno, ename, deptno, sal*12 + nvl(comm, 0) from emp where deptno=10";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//System.out.println("EMPNO ENAME DEPTNO SAL*12+NVL(COMM,0)");
while(rs.next()) { //행
System.out.printf("%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\n",
// 인덱스 : 출력 컬럼의 순서
rs.getString(1),
rs.getString(2),
rs.getString(3),
rs.getString(4));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(rs != null) try {rs.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
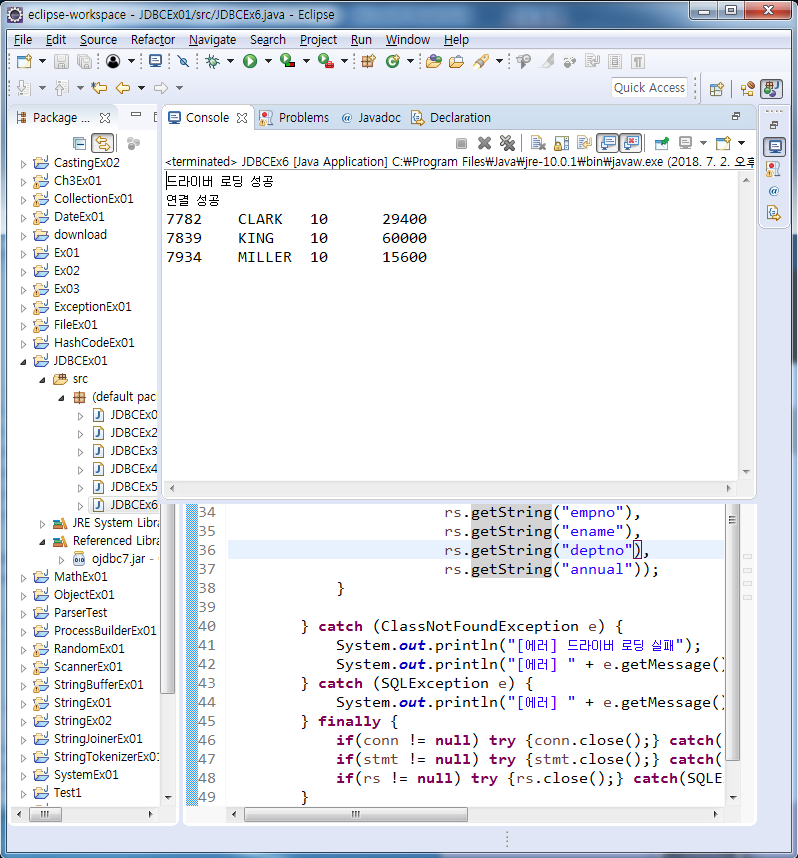
String sql = "select empno, ename, deptno, sal*12 + nvl(comm, 0) as annual from emp where deptno=10";
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//System.out.println("EMPNO ENAME DEPTNO SAL*12+NVL(COMM,0)");
while(rs.next()) { //행
System.out.printf("%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\n",
// 인덱스 : 출력 컬럼의 순서
rs.getString("empno"),
rs.getString("ename"),
rs.getString("deptno"),
rs.getString("annual"));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(rs != null) try {rs.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
searchEname 클래스 제작
실행을 시키면 사원명 -> smi
* 소문자입력
* 찾는 사원이 없으면 없다고 출력
사원번호, 사원명, 직책, 급여가 표시되는 프로그램
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class searchEname {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
String name = "";
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//String sql = String.format("update dept2 set dname='%s' where deptno=%s ", "총무", "60");
System.out.println("찾는 사원의 이름을 입력하시오 : ");
name = scan.nextLine();
String sql = String.format("select empno, ename, job, sal from emp where lower(substr(ename, 1, 3)) = '%s'", name);
rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);
if(rs.next()) {
System.out.printf("%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\n",
// 인덱스 : 출력 컬럼의 순서
rs.getString(1),
rs.getString(2),
rs.getString(3),
rs.getString(4));
} else {
System.out.println("찾는 사원이 없습니다.");
}
scan.close();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(rs != null) try {rs.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
PreparedStatement를 사용한 쿼리 실행
preparedStatement insert, update, create에 많이 사용
JDBCEx7 - PreparedStatement
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx7 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
// statement와 동작은 똑같다. 다만 미리 만들어 두고 데이터를 후에 넣는다는것이 다르다
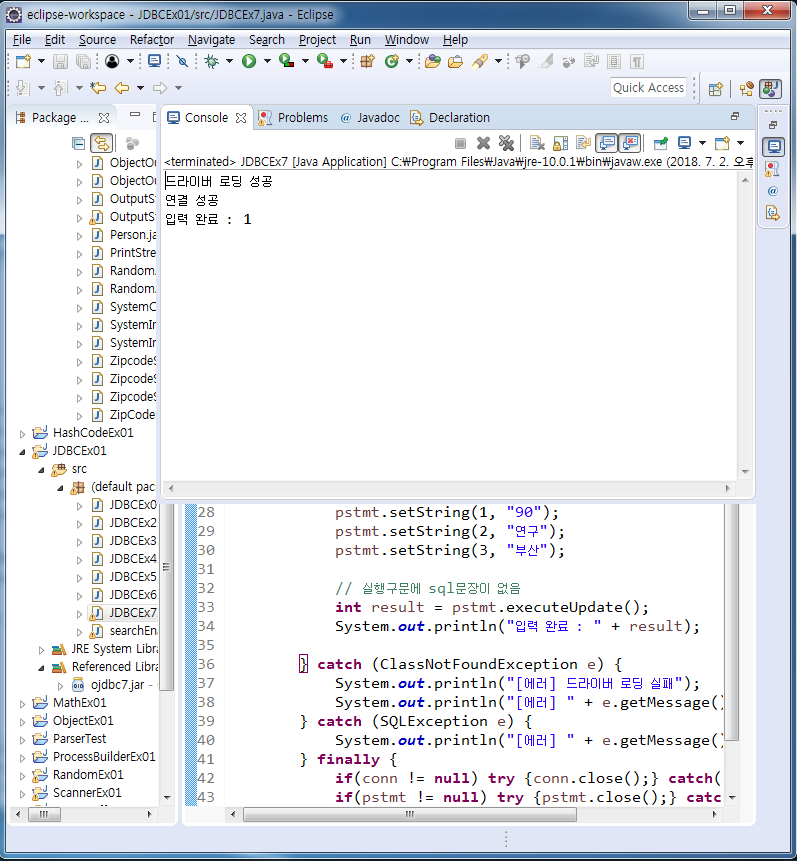
String sql = "insert into dept2 values(?, ?, ?)";
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, "90");
pstmt.setString(2, "연구");
pstmt.setString(3, "부산");
// 실행구문에 sql문장이 없음
int result = pstmt.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("입력 완료 : " + result);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(pstmt != null) try {pstmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}

JDBCEx8 - searchEname과 같이 특정 문자를 입력하여 like로 해당 문자가 포함된 사원명의 데이터 불러오기
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx8 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
ResultSet rs = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
// statement와 동작은 똑같다. 다만 미리 만들어 두고 데이터를 후에 넣는다는것이 다르다
//String sql = "select empno, ename, job, deptno from emp where ename = ?";
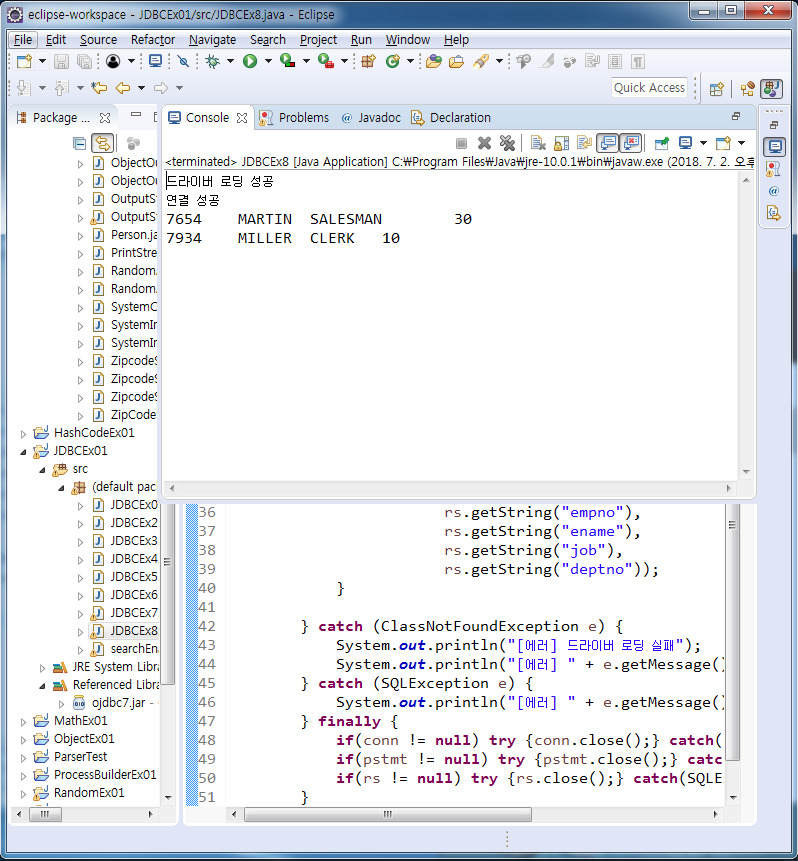
String sql = "select empno, ename, job, deptno from emp where ename like ?";
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
pstmt.setString(1, "M%");
rs = pstmt.executeQuery();
while(rs.next()) {
System.out.printf("%s\t%s\t%s\t%s\n",
rs.getString("empno"),
rs.getString("ename"),
rs.getString("job"),
rs.getString("deptno"));
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(pstmt != null) try {pstmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(rs != null) try {rs.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
ZipcodeSearch
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class ReadZipcode {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
String sql = "insert into zipcode values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("./zipcode_seoul_utf8_type2.csv"));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
//System.out.println(line);
String[] lines = line.split(",");
pstmt.setString(1, lines[0]);
pstmt.setString(2, lines[1]);
pstmt.setString(3, lines[2]);
pstmt.setString(4, lines[3]);
pstmt.setString(5, lines[4]);
pstmt.setString(6, lines[5]);
pstmt.setString(7, lines[6]);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
System.out.println("입력 완료");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(br != null) try{br.close();} catch(IOException e) {};
if(conn != null) try{conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(pstmt != null) try{pstmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}
JDBCEx09 - zipcode내 항목 만들기
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class JDBCEx9 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
//String sql = "create table dept3 (deptno number(2), dname varchar2(14), loc varchar2(13))";
StringBuffer sql = new StringBuffer("create table zipcode (");
sql.append(" zipcode char(7) NOT NULL, ");
sql.append(" sido varchar2(6) NOT NULL, ");
sql.append(" gugun varchar2(27) NOT NULL, ");
sql.append(" dong varchar2(39) NOT NULL, ");
sql.append(" ri varchar2(67), ");
sql.append(" bunji varchar2(18), ");
sql.append(" seq number(5) NOT NULL ");
sql.append(" )");
stmt.executeUpdate(sql.toString());
System.out.println("성공");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] 드라이버 로딩 실패");
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} catch (SQLException e) {
System.out.println("[에러] " + e.getMessage());
} finally {
if(conn != null) try {conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try {stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
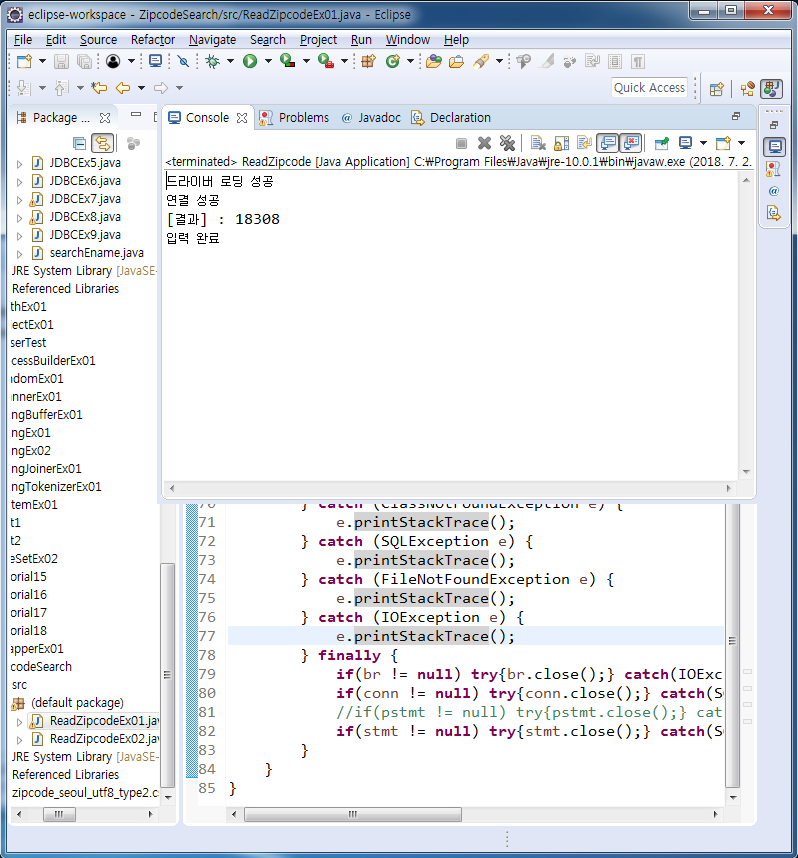
}ReadZipcodeEx01 - JDBCEx09에서 만든 zipcode 항목에 zipcode_seoul_utf8_type2.csv 데이터를 statement를 사용하여 데이터 집어 넣는 방법
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.sql.Statement;
public class ReadZipcodeEx01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
stmt = conn.createStatement();
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("./zipcode_seoul_utf8_type2.csv"));
String line = null;
int result = 0;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
String[] adds = line.split(",");
String zipcode = adds[0];
String sido = adds[1];
String gugun = adds[2];
String dong = adds[3];
String ri = adds[4] == null ? "" : adds[4];
String bunji = adds[5] == null ? "" : adds[5];
String seq = adds[6];
String sql = String.format("insert into zipcode values ('%s', '%s', '%s', '%s', '%s', '%s', '%s')",
zipcode, sido, gugun, dong, ri, bunji, seq);
result += stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
}
System.out.println("[결과] : " + result);
System.out.println("입력 완료");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(br != null) try{br.close();} catch(IOException e) {};
if(conn != null) try{conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(stmt != null) try{stmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}

ReadZipcodeEx02 - JDBCEx09에서 만든 zipcode 항목에 zipcode_seoul_utf8_type2.csv 데이터를 PreparedStatement를 사용하여 데이터 집어 넣는 방법
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class ReadZipcodeEx02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedReader br = null;
String url = "jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl";
String user = "scott";
String password = "tiger";
Connection conn = null;
PreparedStatement pstmt = null;
try {
Class.forName("oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver");
System.out.println("드라이버 로딩 성공");
conn = DriverManager.getConnection(url, user, password);
System.out.println("연결 성공");
String sql = "insert into zipcode values (?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?, ?)";
pstmt = conn.prepareStatement(sql);
br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader("./zipcode_seoul_utf8_type2.csv"));
String line = null;
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
//System.out.println(line);
String[] lines = line.split(",");
pstmt.setString(1, lines[0]);
pstmt.setString(2, lines[1]);
pstmt.setString(3, lines[2]);
pstmt.setString(4, lines[3]);
pstmt.setString(5, lines[4]);
pstmt.setString(6, lines[5]);
pstmt.setString(7, lines[6]);
pstmt.executeUpdate();
}
System.out.println("입력 완료");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(br != null) try{br.close();} catch(IOException e) {};
if(conn != null) try{conn.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
if(pstmt != null) try{pstmt.close();} catch(SQLException e) {};
}
}
}

'Web & Mobile > JSP' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Lecture 33 - JSP(2) 우편번호검색, DatabaseMetadata, Callable (0) | 2023.06.20 |
|---|---|
| Lecture 62 - JSP(20) MyBatis 이용한 게시판, 사진이 나오는 앨범 게시판 (0) | 2019.06.14 |
| Lecture 61 - JSP(19) ZipcodeController, MyBatis 설정법, Mapper (0) | 2019.06.13 |
| Lecture 60 - JSP(18) JSTL, 우편번호검색 (0) | 2019.06.12 |
| Lecture 59 - JSP(17) EL, <%= %>, EL을 Model1 게시판에 적용, JSTL (0) | 2019.06.11 |




댓글